Tools to help you implement design thinking in education
Educators have a unique challenge of teaching and mentoring the next generation of business leaders, activists, and scholars. One important part of this task is to encourage creativity and innovation from a young age, which is often easier said than done. However, one process that will help educators inspire the next generation is design thinking. Design thinking begins with understanding your audience and developing solutions or ideas based on what they need, rather than what you want to create. For educators, this perspective can help your students develop critical thinking and creativity skills they can foster for years to come. Here are five resources that can you help you begin to implement design thinking in your classroom:
- Ideo’s design thinking for educators toolkit
- Business Innovation Factory for educators toolkit
- Stanford d.school
- Readings on design thinking
- Edutopia’s design thinking video collection
(We are currently doing research about teaching design thinking. If you are an educator teaching or helping students learn or use design thinking…please share your experience on our short open-ended survey.)
Keep reading to learn more about design thinking for educators and these five resources.

Design Thinking for Educators
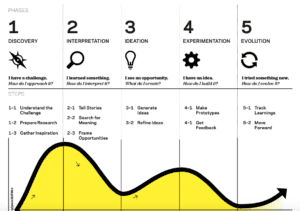
Design thinking has five important “phases” – discovery, interpretation, ideation, experimentation, and evolution. Here is a brief definition of each of these steps:
- Discovery: understanding and researching the problem
- Interpretation: connecting the dots in your research
- Ideation: generating and refining ideas on how to solve the problem
- Experimentation: testing your ideas, collaborating with others, getting feedback
- Evolution: drawing conclusions, evolving your ideas, moving forward
For educators, this process can be implemented into classroom lessons and projects to help students generate and innovate their ideas. Students will begin to learn how to adapt and solve problems after conducting research and analyzing what they discovered. This, in turn, will prepare them for a future that is heavily focused on user experience and innovative solutions to customer problems.
Ideo’s Design Thinking for Educators Toolkit
 One design thinking resource for educators is from leading design and innovation company Ideo. Ideo provides a toolkit for educators that includes examples of ways in which other teachers implemented the design thinking process in their classroom, as well as tips and techniques to make your own implementation successful.
One design thinking resource for educators is from leading design and innovation company Ideo. Ideo provides a toolkit for educators that includes examples of ways in which other teachers implemented the design thinking process in their classroom, as well as tips and techniques to make your own implementation successful.
Click here to download the toolkit.
Click here to view Ideo’s educators website.
Business Innovation Factory TD4Ed
The Business Innovation Factory has an online resource website that provides examples of how one school used design thinking to innovate their curriculum. You can access the website here.
Stanford d.school
 Stanford University’s d.school is a unique place for design thinking, creativity, and innovation to take place. They also offer a wide range of resources to help educators with their design thinking efforts. Their Design Thinking Bootcamp Bootleg is a good place for anyone new to design thinking to start.
Stanford University’s d.school is a unique place for design thinking, creativity, and innovation to take place. They also offer a wide range of resources to help educators with their design thinking efforts. Their Design Thinking Bootcamp Bootleg is a good place for anyone new to design thinking to start.
Also check out their K-12 guide to design thinking.
Readings on design thinking
There are many books and articles out there that cover the topic of design thinking. Here are some that may help you as an educator. Please comment with some of your favorite educator resources on design thinking.
“What Can We Learn From Libraries That Use Design Thinking?,” is a resource published by Syracuse University’s online Master of Science in Library and Information Science program. The resource defines design thinking, reviews the design thinking process and provides many examples of problems solved through the process. This article is great for libraries and can help you understand design thinking and how to apply it in their own lives.
Here are other design thinking related articles helpful for educators:
- The Third Teacher
- 100 Things Every Designer Should Know About People
- “Teaching Kids Design Thinking, So They Can Solve the World’s Biggest Problems”
- “Teaching and Learning through Design Thinking”
Edutopia’s Design Thinking Video Collection
Edutopia provides a 5 minute video series focused around design thinking for educators. You can view the collection here.
Also check out this design thinking for educators Vimeo channel created by IDEO for another video collection.
We’ve been building a video collection on design thinking for teachers. Check it out and consider it a “prototype” of a rough online course you can use to learn more about applying design thinking for students in and out of the classroom. It includes many of the best videos we’ve found over the years focused on design thinking in education.
BONUS! If you are looking for a software or application to help students run an actual design thinking project. See this link from Sprintbase to get in touch about their educator program.
With these five design thinking for educators tools, you will be well on your way to implementing this innovative process in your classroom lessons and projects. Through design thinking, you can set your students up for success in the future by encouraging creativity, analysis, research, experimentation, and implementation in class.
Design Thinking and Education
I was asked “how design thinking impacts learning through a more creative “human first” approach at all levels.” Here’s a detailed response that I resonate with and is a decent synthesis of what I’ve experienced doing this work over 15 years.
Design thinking impacts learning through a creative, “human-centered” approach by fundamentally reorienting the way learners engage with content, each other, and the challenges they face. It fosters environments where creativity, empathy, and problem-solving are prioritized, making learning more meaningful and applicable at all levels. Here’s how:
1. Empathy-Driven Learning
Design thinking starts with empathy, which means understanding the needs, motivations, and pain points of those involved in the learning process. By placing a strong emphasis on understanding the learner’s perspective, it encourages educators and facilitators to create content and learning experiences that are more relevant and impactful. This approach can:
- Make learning more personalized and responsive to the individual’s needs.
- Help students feel seen and understood, which fosters a stronger connection and engagement.
2. Promoting Creative Confidence
One of the core goals of design thinking is to unlock creative potential in every learner. It builds creative confidence by encouraging learners to take risks, experiment, and embrace failure as part of the learning process. This contrasts with traditional learning models that may focus more on correct answers and minimizing mistakes. A creative, human-first approach:
- Provides safe spaces for exploration, reducing fear of failure.
- Encourages iterative learning through prototyping and feedback, leading to deeper understanding.
- Empowers students to see themselves as active creators rather than passive consumers of knowledge.
3. Active and Experiential Learning
Design thinking is inherently hands-on and experiential. It moves beyond lecture-based or passive learning models by integrating activities like brainstorming, prototyping, and role-playing, making learning more dynamic. This promotes engagement and retention of information because learners:
- Learn by doing, which deepens comprehension and skill acquisition.
- Encounter real-world scenarios, preparing them to apply their knowledge in varied contexts.
4. Problem-Based Learning and Real-World Application
A human-centered approach often ties learning to solving real-world problems that matter to learners. This relevance drives motivation and makes learning feel purposeful. With design thinking:
- Learners tackle authentic challenges, making the content more tangible and applicable.
- Collaboration is emphasized, mirroring the teamwork needed in real-world problem-solving.
- It fosters a mindset shift from focusing on “What do I need to learn?” to “How can I use what I know to create impact?”
5. Encouraging a Growth Mindset
Because design thinking revolves around iterative testing and refining ideas, it naturally cultivates a growth mindset. Learners are encouraged to view challenges and setbacks as opportunities to grow, reframe, and adapt their understanding. This mindset:
- Builds resilience, adaptability, and a willingness to tackle ambiguous challenges.
- Enhances metacognitive skills as learners reflect on their thinking and problem-solving processes.
6. Building Collaboration and Social Learning
Design thinking is inherently collaborative, emphasizing co-creation and the inclusion of diverse perspectives. This approach builds a culture of shared learning, where participants learn from each other as much as from the content itself. In a learning environment, this:
- Helps break down silos and fosters cross-disciplinary understanding.
- Strengthens communication, negotiation, and team-building skills.
- Encourages learners to appreciate multiple viewpoints, enhancing cognitive flexibility.
7. Creating Learner-Centered Environments
Design thinking allows learning experiences to be more flexible, adaptive, and responsive to feedback. This learner-centered approach shifts the power dynamics in the classroom or workshop:
- Educators become facilitators or guides rather than simply disseminators of information.
- Learners are empowered to co-create their learning experiences, leading to higher ownership and intrinsic motivation.
8. Transforming Leadership and Culture at All Levels
Finally, a human-centered design approach impacts not just individual learners but also the culture of learning within organizations and institutions. When design thinking is implemented at all levels, it transforms the way leadership, faculty, and even administrative structures think about learning:
- It encourages a more agile, learner-focused strategy for developing curricula or programs.
- It fosters environments that prioritize innovation, inclusivity, and continuous improvement.
- It aligns leadership strategies with empathy, making educational institutions more attuned to the needs of both staff and students.
Key Takeaway
By embracing a “human-first” mindset, design thinking fundamentally reshapes the learning experience, making it more engaging, relevant, and transformative. It brings creativity to the forefront, shifts focus toward empathy, and empowers learners at all levels to develop the skills and mindsets they need to navigate complex, ever-evolving challenges.
For more information, contact us or check out our innovation and design thinking resource blog.
